Discover how blockchain technology works, its key components like hashing and consensus, and how it's transforming industries beyond cryptocurrency with security, transparency, and decentralization.
Since its emergence in 2008 with the birth of Bitcoin, blockchain technology has captured the world's attention for its ability to transform not only finance, but also sectors such as healthcare, government and supply chain. What makes it so special? Its secure, transparent and decentralized structure. This article will guide you through the basics of blockchain and its applications beyond cryptocurrencies.
Blockchain, or blockchain, is a distributed digital ledger that records information in a secure, transparent and virtually unalterable way. It is composed of blocks connected to each other chronologically, where each block contains:
By modifying a block, the connection with the following blocks is broken, making any tampering attempt obvious.

Although hashing allows to detect tampering, attackers could recalculate hashes quickly. This is where a second level of security comes into play: the Proof of Work
This mechanism requires high computational power to create new blocks. For example, in Bitcoin, each block requires about 10 minutes to validate. Thus, altering the entire chain becomes unfeasible.
Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, where all nodes share a copy of the chain. A new block is accepted only if the majority of nodes verify it, ensuring consensus and resistance to tampering.

Although it was designed for the exchange of cryptocurrencies, today blockchain drives new solutions:
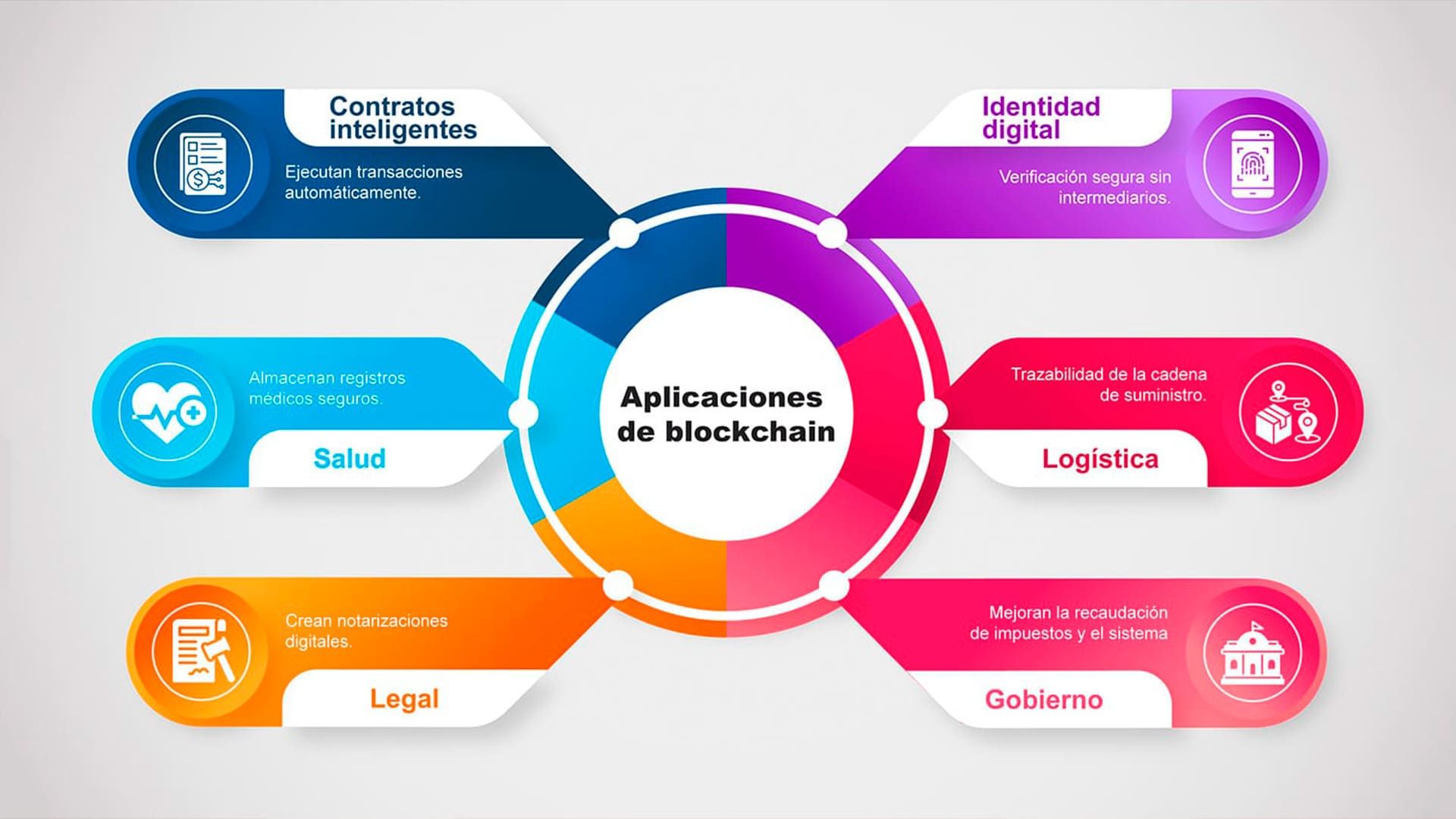
Blockchain is not just a technological fad: it represents a revolution in how we understand trust, data and decentralization. Its growth and adaptation in different industries show its transformative potential. Understanding how it works is key to anticipating the innovations that will shape the digital future.